A hybrid cloud allows CIOs, IT managers, IT administrators, etc to build on the advantages of both public and private data centre environments while architecting unique solutions for multiple business requirements. Some issues to consider when choosing a hybrid cloud solution are:
• Multi-Cloud Architecture: Does your enterprise business organisation operate hybrid cloud orchestration with multi-cloud functionality where more than one public cloud service provider is utilised?
• Data Privacy: Does your business keep sensitive internal information from clients, partners, employees, and manufacturing facilities on private cloud hardware while still utilising the innovative new platform services from public cloud hosting companies in production operations remotely in a hyper-scale facility?
• Network Security: Does your business need to build a unified corporate security policy with firewalls,content filters, VPN, anti-virus, & storage encryption applied across remote cloud hardware resources?
Hybrid cloud networking can also include firewall integration and VPN support for employee connections to third-party websites in order to access SaaS and PaaS applications for productivity. Businesses and other complex organisations typically adopt virtualisation in data centre operations in order to build hybrid cloud architecture across vendor hardware resources more quickly, securely, and cost-efficiently.
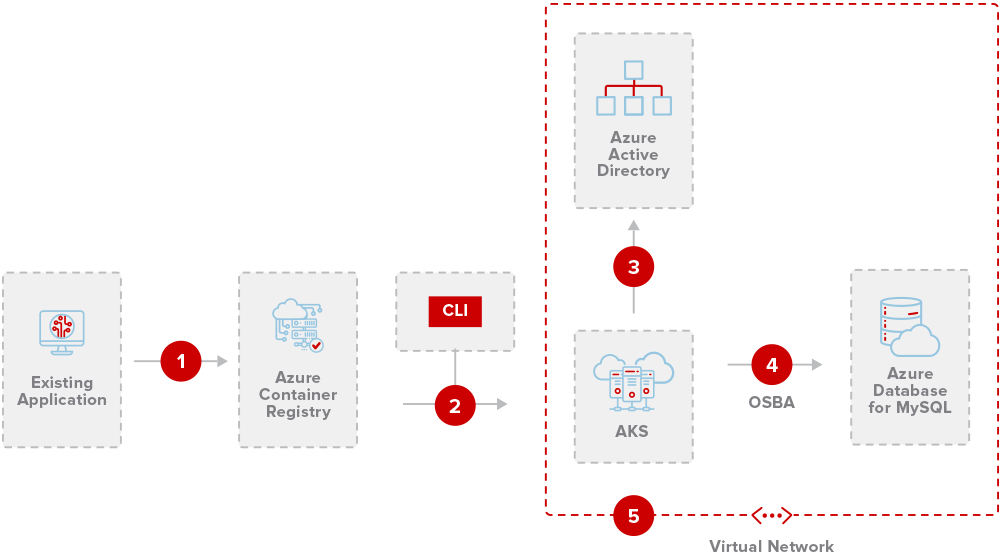
Virtualisation allows network administrators to make better use of hardware allocations on web servers and to automate data centre processes to scale elastically with web traffic requirements in production. Hypervisor virtualisation using VMs (virtual machines) and container virtualisation with Docker/Kubernetes are the two leading solutions to hybrid cloud orchestration for enterprise data centres. AWS’s EC2, EKS, S3, and DBaaS (Database-as-a-Service) platforms compete with Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and VMware products as the most popular public cloud service providers for hybrid cloud integration.
One of the key benefits of a hybrid cloud is the agility it offers to enterprise corporations in bringing new software products to market. Being able to adapt and change direction quickly is a key requirement in a modern digital business environment. Hybrid cloud’s ability to combine public clouds, private clouds, and on-premise resources and cloud connection solutions, gives complex business organisations the agility needed for a competitive advantage.
Building a hybrid cloud offers an organisation a big range of potential benefits including:
• Flexibility – The ability to distribute workloads across public and private environments based on security, efficiency, and cost.
• Scalability – The ability to outsource workflow peaks to public cloud environments and to scale resources up and down as the business demands change.
• Reliability – Less likelihood of downtime because services are distributed across multiple public and private data centres.
• Security – By outsourcing non-sensitive workloads to the public cloud, sensitive workloads can be run on dedicated resources in private clouds.
• Affordability – Outsourcing to public cloud eliminates the need to purchase and maintain additional resources to handle short term spikes in demand.
• Continuity – Business continuity is not interrupted during a failure or disaster, as data is still accessible with little or no downtime.
• Opportunity – Barriers to innovation are reduced because new concepts can be tested and prototyped without great expense in a cloud environment, then rapidly deployed and measured for success.
• Accessibility – The cloud offers the advantage of anywhere, anytime access (important with an increasingly mobile workforce).
Hybrid cloud architecture can help retail sellers manage peak web traffic for ecommerce websites and mobile applications through elastic web servers and DBaaS products. It can also increase data privacy protections for ecommerce companies or ensure compliance with local auditing and regulatory requirements for regional businesses.
Hybrid cloud supports innovation in the software development lifecycle across enterprise companies, startups, non-profits, educational institutions, healthcare groups, and government organizations.
Successful real-world examples for when a hybrid cloud solution could be beneficial include:
• Affordable disaster recovery and business continuity – Using a hybrid cloud setup where on-premise data fails over to a public cloud in an emergency.
• Cost-effective archiving – Cheaply putting at-rest data in a hybrid cloud for long periods of time for future analysis or to satisfy compliance requirements.
• Application development – Using public clouds to speed up the development process and then moving applications back to the on-premises data centre for production deployment.
• Cloud bursting – Running applications in a private cloud until a predetermined demand level for resources is reached, then causing them to fail over to a public cloud service.
• Separating workloads – using a public cloud for dynamic and non-sensitive workloads and leaving less volatile or more sensitive workloads on a private cloud.
• Big Data processing – using a public cloud for the majority of big data analysis and leaving sensitive big data on a private cloud.
• Moving to the cloud – adding workloads to a public cloud gradually while expanding the remote presence as needed on public and private clouds or a mixture of both.
• Dealing with temporary demand – allocating public cloud resources for short term projects at a lower cost than possible with your own private data centre.
• Being prepared for the future – having the resources to be able to match your data management needs with the most appropriate public, private or on-premise resources.
• Speed to market – implementing best practices for Agile project management and DevOps in the software development lifecycle with CI/CD, version control, and automated testing for software code.
• Cost transparency and control – utilising public cloud “pay as you go” billing with reserved instances and competitive bidding for spot pricing on hardware resources.
• Security and regulation, data sovereignty – ensuring business compliance with ISO 9000/14000 regulations, HIPAA for healthcare groups, APRA for financial institutions, GDPR for data privacy and cookie usage, or other required auditing standards.
• Data security – The hybrid cloud model also allows you to keep data secure on local servers for internal business requirements while adopting the latest web development, cloud hosting, and programming tools for software applications.
• Public for scale – guarantees uptime of software services by offloading web traffic in peak operations to public cloud hardware using containers or VM orchestration.
• Innovation – integrate API calls across the service mesh or over the internet to build new functionality and features for web/mobile apps like AI/ML and serverless support.
• Software-defined networking (SDN) – build multi-cloud architecture across public cloud vendor hardware with containers, Kubernetes, and VMs for SDDC outsourcing.
While there are many opportunities associated with building a hybrid cloud, there may also be challenges an organisation will need to overcome, including;
• Security – Security is definitely a benefit of hybrid cloud when compared to a public cloud solution. In particular, if the private cloud is delivered by a Managed Service Provider (MSP) like Canon Business Services (formerly Harbour IT), then data may move out of the customer data centre and into our data centre/private cloud securely.
• Preparation – It’s important to remember that with a hybrid solution you may need to take some precautionary steps to ensure maximum data security is applied to your data in the public cloud.
• Compatibility – Care must be taken in the choice of public cloud services and their API integration capabilities, or they may not perform optimally with on-premise infrastructure.
• Scalability – A careful eye must be kept on environment automation to avoid overshooting scalability limits of data that is required to be kept in the private cloud due to compliance and security reasons.
• Offloading – Because the public cloud scalability is hyper-scale, there are more areas open to public cloud offloading and less likelihood that you will run into scalability issues.
• Compliance – Depending on what type of business or industry you are in, compliance regulations may prevent you from using a public cloud or storing data offsite.
• Integration – Depending on the type of data and applications you currently have, there may be integration problems to overcome when transferring to a hybrid cloud environment.
• Networking – You may also need to upgrade your network bandwidth to prevent highly active applications in the cloud from bottlenecking other applications.
Complex business organisations that adopt hybrid cloud architecture or multi-cloud solutions without an MSP to manage the migration will likely encounter problems with:
• Understanding – Without sufficient education, some organisations may struggle to understand the nature of cloud computing and how to exploit its full potential.
• Training – A different skill set is required with hybrid cloud technology, which may be in short supply until appropriate training can produce more qualified candidates.
• Expertise – If an organisation does not have the necessary skills in-house, they will have to hire outside experts to build their hybrid cloud, which can be expensive.
• Hardware – If the private cloud is to be on-premise, rather than operated by an offsite provider, then all necessary hardware will need to be purchased, programmed, and maintained. This is a potentially expensive exercise.
• Optimisation of costs – The continuous improvement of the hybrid cloud set up to ensure costs are managed and performance is optimised may be harder for an organisation without an MSP.
• Support – The ability to ensure that you’re resourcing the management of the operations correctly, including monitoring, SLA’s (for lines of business), DR, BU (managed by the MSP) etc may be reduced.
• Complexity – MSP’s should have a Cloud Management Platform featuring a suite of integrated software tools they can offer to businesses, which could assist with resource management, service management, and more.
For these reasons, working with a managed service provider such as Canon Business Services (CBS) could greatly improve the efficacy and management of your hybrid cloud solution.