Cybersecurity employs SIEM and XDR for threat protection. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) analyses security data and logs for incident management, while XDR integrates multiple data sources for advanced threat detection. Key differences lie in their data analysis approaches and coverage breadth, enhancing overall security operations.
Table of Contents
1. Understanding SIEM
2. Exploring XDR
3. Key Differences Between SIEM and XDR
4. The Evolution of Cybersecurity Technologies
5. Traditional vs. Modern Security Solutions
6. Core Components and Functionalities
7. The Complementary Nature of SIEM and XDR
8. Deployment and Integration Strategies
9. Conclusion
SIEM, or Security Information and Event Management is central to cybersecurity, analyse log data from diverse sources like firewalls and servers to detect security incidents. These tools enable real-time network monitoring, aiding security teams in rapid response to threats, but may struggle with new, undefined threats beyond established patterns.
XDR enhances cybersecurity by expanding SIEM capabilities with additional data sources like endpoints, IoT devices, and cloud services. These solutions offer a comprehensive view of an organisation's security posture, using advanced analytics, machine learning, and behavioural analysis to improve threat detection and response, catching threats that traditional SIEM might miss.
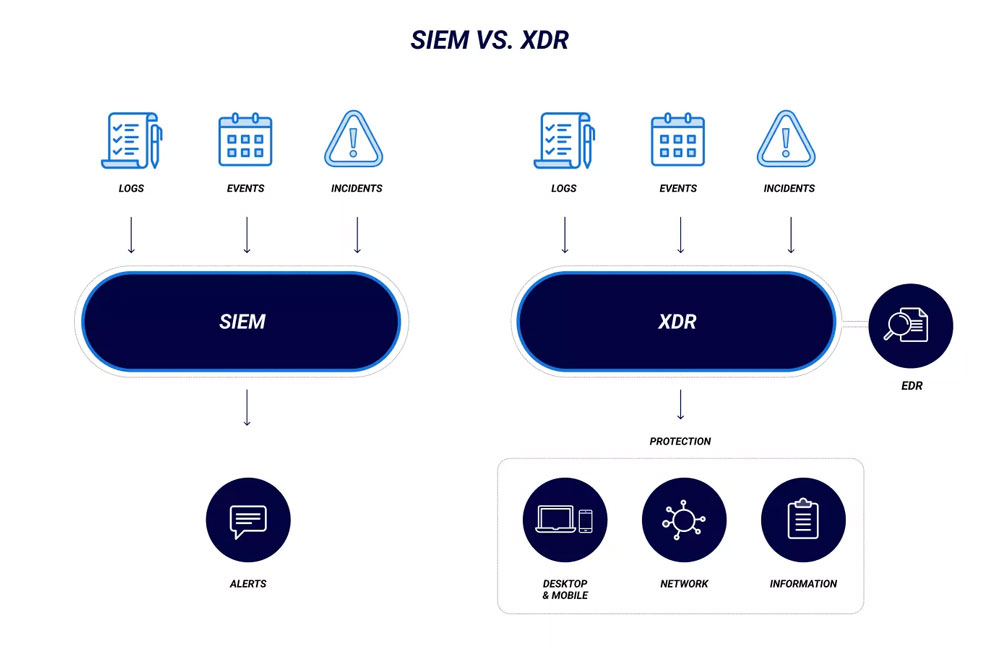
While both SIEM and XDR are used to detect and respond to security incidents, there are some key differences between the two approaches. One of the main differences is the scope of data collection. SIEM solutions typically focus on data from servers, firewalls, and other network devices. XDR solutions, on the other hand, aim to collect data from a much broader range of sources, including endpoints and cloud services.
Another key difference is the use of analytics. SIEM tools typically use rule-based analytics to detect security threats. XDR solutions, on the other hand, use advanced analytics such as machine learning and behavioural analysis to improve threat detection and response.
Finally, XDR solutions are often more focused on automated response, whereas SIEM solutions typically require more human intervention in the incident response process. This is due to the increased complexity of XDR solutions, which can make it difficult to determine the most appropriate response in certain situations.
Despite these differences, both SIEM and XDR solutions are important tools in the fight against cyber threats. By using these tools in combination with other cybersecurity measures such as employee training and network segmentation, organisations can significantly improve their security posture and better protect themselves from cyber-attacks.
SIEM emerged in the late 1990s and early 2000s, addressing the need for enhanced security monitoring and incident response amid escalating cyber threats and regulations. Initially, SIEM solutions focused on log management, event correlation, and reporting, forming a foundational approach to cybersecurity.
As the internet's prevalence grew and reliance on digital infrastructure increased, the demand for robust cybersecurity solutions intensified. SIEM gained popularity among organisations for providing a centralised platform to monitor and respond to security events, enhancing their overall security posture.
However, the evolving sophistication of cyber threats revealed limitations in SIEM systems. They often struggled to detect and respond effectively to advanced persistent threats (APTs) and other complex attacks, highlighting the need for more advanced security solutions.
SIEM solutions, despite their evolution, face limitations in modern complex IT environments, leading to the rise of XDR (Extended Detection and Response). XDR addresses SIEM's shortcomings by adapting to the varied devices and applications present in current IT landscapes.
XDR stands apart from traditional SIEM by offering a more comprehensive and proactive defense against cyber threats. It moves beyond SIEM's primary focus on log management and event correlation, aiming to deliver a holistic view of an organisation's security posture, crucial for today's diverse digital ecosystems.
XDR's strength lies in its integration of data from endpoints, network traffic, and cloud applications, providing a fuller picture of security. This integration enables quicker, more effective threat detection and response, marking a significant advancement over traditional SIEM systems.
The emergence of advanced persistent threats (APTs) and sophisticated cyber-attacks has catalysed a shift from traditional IT security solutions like SIEM to more advanced approaches such as XDR. While SIEM solutions, focusing on log management and event correlation, remain in use, they often fall short against complex threats. In contrast, XDR solutions provide comprehensive threat detection and response capabilities, leveraging automated response to mitigate the impact of cyber attacks effectively.
The increasing reliance on cloud-based infrastructure further drives this transition. Traditional security tools like firewalls become less effective in cloud environments. XDR solutions, however, are tailored for these settings, offering robust threat detection and response, even in complex multi-cloud scenarios.
This evolution in cybersecurity technology reflects the growing complexity of IT environments, the rise of advanced threats, and the importance of cloud infrastructure. SIEM solutions, once the go-to, now give way to XDR and other modern security solutions, equipping organisations with a more proactive and encompassing defense against cyber threats.
When it comes to cybersecurity, it's important to have the right tools in place to protect your organisation from potential threats. Two popular solutions for threat detection and response are SIEM and XDR.
SIEM solutions encompass several key components like log collection, normalisation, correlation, and analysis. These elements gather data from varied sources, format it uniformly, and analyse in real-time to detect security threats. Integral to SIEM, these processes enable efficient threat identification and response, with reporting and alerting functionalities aiding security teams.
Log collection is crucial, aggregating data from network devices, servers, and endpoints. Normalisation of this data facilitates easier analysis and correlation, enhancing the detection process. Correlation, a vital aspect of SIEM, identifies patterns and anomalies that could indicate security risks.
Furthermore, SIEM's analysis capabilities, incorporating machine learning and advanced techniques, detect threats in real-time. This allows security teams to swiftly respond to incidents and identify potential vulnerabilities, reinforcing the IT environment's security.
XDR solutions typically include a wider range of components and functions than SIEM solutions. In addition to log collection and analysis, XDR solutions also include endpoint detection and response (EDR) capabilities, cloud security monitoring, and other advanced features like machine learning and behavioural analysis. These components work together to provide a more comprehensive view of the IT environment and to improve threat detection and response.
Endpoint detection and response (EDR) is a critical component of XDR solutions, as it allows security teams to detect and respond to threats on individual endpoints, such as laptops and mobile devices. This is particularly important in today's remote work environment, where employees may be accessing corporate resources from a variety of locations and devices.
Cloud security monitoring is another key component of XDR solutions, as it allows security teams to monitor cloud environments for potential security threats. As more organisations move their applications and data to the cloud, it's important to have the right tools in place to protect these resources from potential threats.
While there are some key differences between SIEM and XDR, the two approaches are not mutually exclusive. In fact, many organisations use both SIEM and XDR to complement each other and improve their overall security posture. By using SIEM for network-centric monitoring and XDR for endpoint and cloud monitoring, organisations can achieve a more comprehensive view of their IT environment and increase their ability to detect and respond to security threats.
By combining the log collection and analysis capabilities of SIEM with the endpoint detection and response (EDR) and cloud security monitoring capabilities of XDR, organisations can improve their ability to detect and respond to a wide range of security threats. This can help to reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents, and can also help to improve overall IT security posture.
SIEM solutions can be deployed in a variety of ways, including on-premises, cloud-based, and hybrid deployments. On-premises deployments typically involve installing software on dedicated hardware within the organisation's data center. Cloud-based deployments involve using a SIEM service provided by a third-party vendor. Hybrid deployments combine elements of both on-premises and cloud-based deployments.
XDR solutions are often cloud-based, although some vendors also offer on-premises and hybrid deployment options. In most cases, the data collected by XDR solutions is transmitted to the vendor's cloud for analysis. However, some XDR vendors also offer on-premises analytics capabilities for organisations with strict data security requirements.
Integrating SIEM and XDR solutions can be challenging due to the disparate data sources and analytics approaches used by each. However, there are a number of integration options available. One common approach is to use APIs or other integration methods to allow SIEM and XDR solutions to exchange data and alerts with each other. Another approach is to use a unified security platform that integrates both SIEM and XDR capabilities into a single solution.
When it comes to choosing between SIEM and XDR, there is no one-size-fits-all answer. Both approaches have their strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice will depend on the specific needs and requirements of each organisation. However, by understanding the key differences between SIEM and XDR, as well as their respective components and deployment options, organisations can make more informed decisions about their cybersecurity strategies and improve their ability to detect and respond to security threats.
The key differences between SIEM and XDR are evident in their data collection scope and analytics use. SIEM solutions primarily focus on collecting and analysing log data from servers and network devices, utilizing rule-based analytics geared towards identifying security incidents.
This approach is central to security information management and event management. In contrast, XDR solutions adopt a more extensive approach, gathering data from a wider array of sources, including endpoints, cloud services, and disparate security tools. They employ advanced analytics capabilities, notably machine learning and artificial intelligence, to enhance threat detection and response. This extended detection and analysis of data enables XDR to offer a more comprehensive security solution, effectively addressing complex threats and improving an organisation's overall security orchestration.
SIEM solutions play a pivotal role in enhancing threat detection by meticulously analysing security data and logs sourced from a variety of network components, such as firewalls, servers, and other critical infrastructure. This comprehensive log management and data analytics capability are integral to the functioning of SIEM tools, enabling security teams to conduct real-time network monitoring. Such vigilant surveillance aids in the prompt identification and response to potential security incidents, ensuring rapid incident response. By correlating data from multiple sources, SIEM solutions empower security teams to effectively detect threats, reduce false positives, and manage security alerts, thereby strengthening the overall security posture of an organisation.
XDR solutions offer significant advantages to security teams by integrating diverse data sources, including endpoint data and network traffic, for a comprehensive view of an organisation's security posture. Utilizing advanced analytics, machine learning, and behavioural analysis, XDR enhances threat detection capabilities. This proactive approach in detecting and responding to advanced threats, coupled with automated response capabilities, positions XDR as a superior choice over traditional SIEM solutions, enabling more effective management of complex security incidents and bolstering overall security operations.
Security data is pivotal for both SIEM and XDR solutions, playing a crucial role in threat detection and security operations. SIEM solutions focus on analysing log data and security events for efficient incident management, employing security information management techniques. In contrast, XDR solutions utilize a broader array of security data sources, including endpoint data and cloud data, for enhanced extended detection and response.
This includes leveraging machine learning and artificial intelligence for improved analysis capabilities, enabling security teams to proactively combat complex threats and improve their organisation's security posture. XDR's comprehensive approach to analysing data from disparate security tools offers a significant edge in detecting advanced threats, enhancing response capabilities, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
In the realm of security operations, SIEM and XDR function synergistically, each complementing the other's capabilities. SIEM primarily offers network-centric monitoring, focusing on analysing log data and security events from network devices and servers. This approach is crucial for detecting potential security threats and managing security incidents efficiently.
Conversely, XDR extends the scope of threat detection and response beyond SIEM's range. It incorporates endpoint detection and cloud data analysis, harnessing advanced analytics and machine learning for more effective handling of complex threats. This integration allows security teams to achieve a more comprehensive security posture, enabling proactive threat hunting and enhanced response efforts across various segments of an organisation's IT infrastructure and security orchestration. Together, SIEM and XDR provide a robust, multi-layered defense against a wide array of security threats.